Sustainable Processing
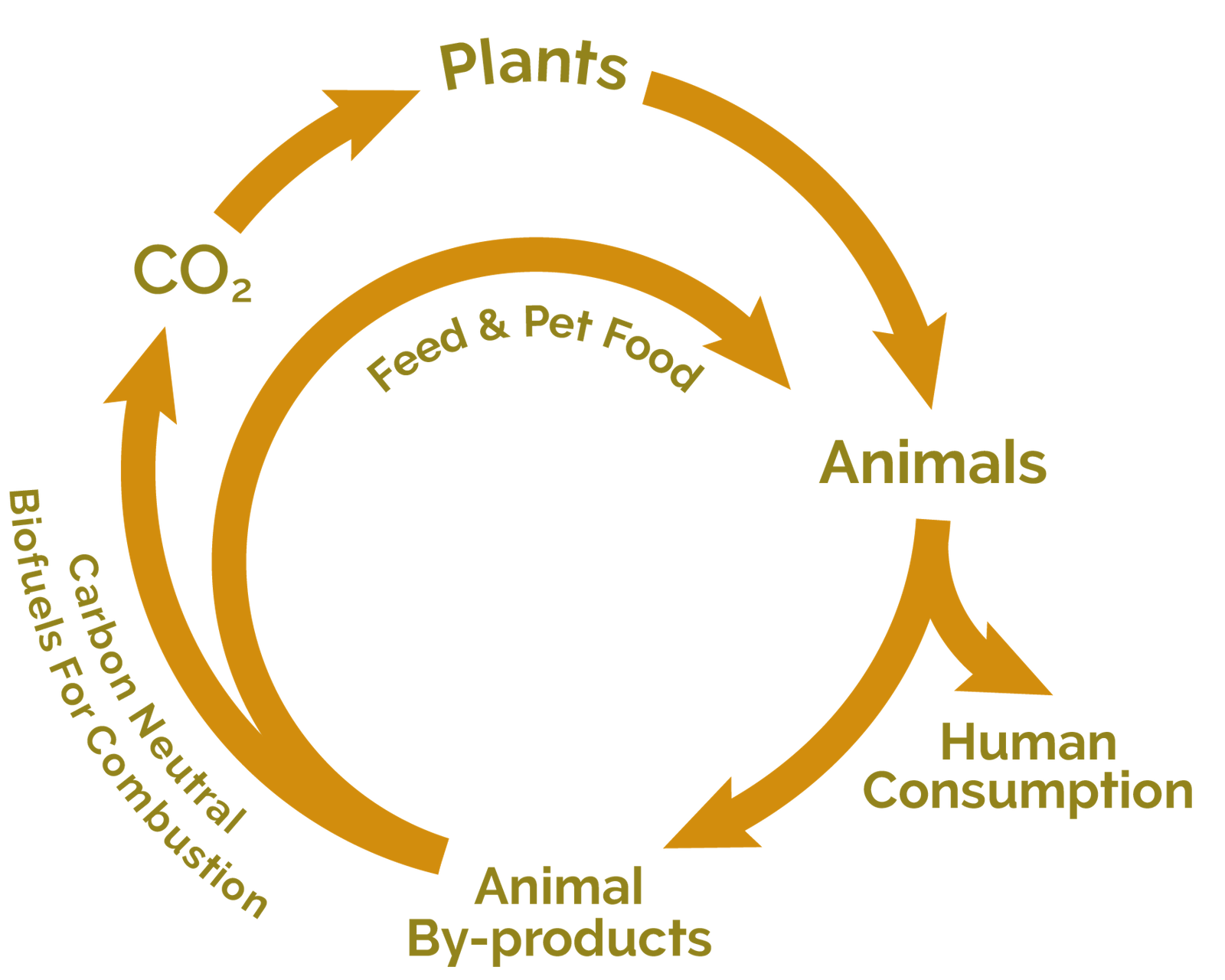
The sustainable processing of ABP and ECP derives products with high added value and maximises nutrient retention within the food value chain.
In processing ABP and ECP from our supply chain partners and returning some of the derived products back to the cycle as feed and fertiliser, we are key in closing the circular bioeconomy loop. This ensures that the precious resources used in raising livestock are not wasted and helps our customers to ethically maximise value from the animal. This contributes to the sustainability of agriculture and food production, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the animal-based food value chain.
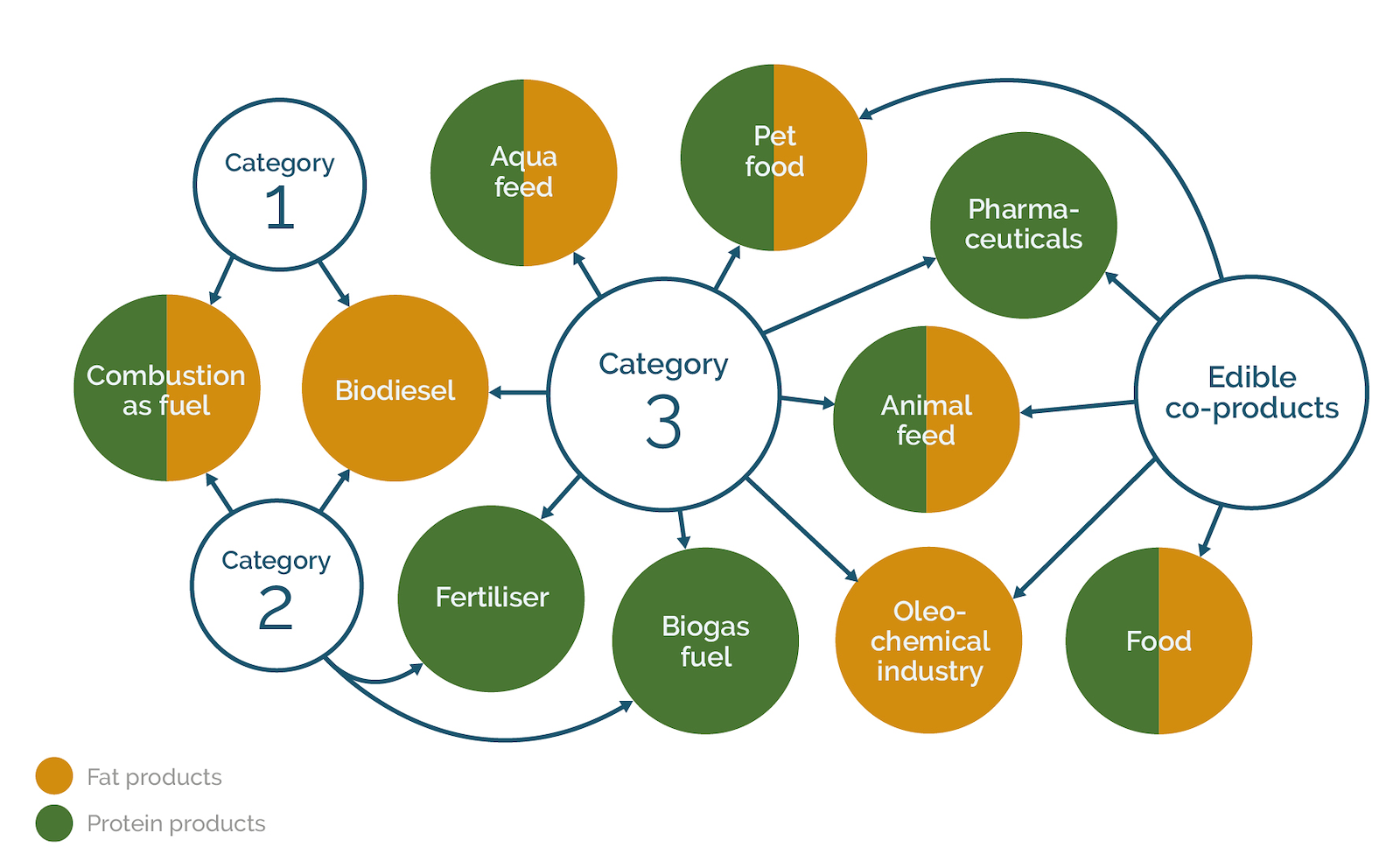
Every year around 18 million tonnes of ABP and ECP are collected from farms, slaughterhouses, butchers, meat processors and other sources. They are then processed and dried by EFPRA members into around 6 million tonnes of products.
With their ability to capture and store carbon, ABP derived products supply a broad array of renewable solutions that can substitute non-renewable and fossil-based materials in products we use every day. These range from traditional products such as food and animal feed ingredients, fertiliser and personal care products to more innovative biofuels and bio-ingredients for the pharmaceutical sector.
ABP and ECP are not classed as waste because they are transformed into useful products but their processing options and applications can be considered in a similar way to the food waste hierarchy. However, it is not as simple as choosing the highest value option.
The derived products and their applications are subject to strict legislative controls, relating to the risk category of the ABP (1 – higher risk; 3 – lower risk) and the species of the source material as illustrated in the figure below.