Climate


We aspire to a climate positive bioeconomy where our natural, low carbon footprint products and renewable fuels help to decarbonise the value chain
The Climate pillar is our key strength. Our members directly support environmental sustainability by utilising by-products that would otherwise be treated as food waste, thus diverting it from landfills and other undesirable disposal options. This helps to maximise the value from the animal and by returning some of the derived products back into the value chain the bioeconomy loop can be closed.
The low carbon footprint of ABP-derived products helps decarbonise the supply chain by substituting higher impact primary resources such as imported vegetable-based feed ingredients like palm oil and soya, chemical based fertilisers and fossil fuels.
The high phosphorus content of PAPs that are utilised in different applications reduces the demand for inorganic phosphorus, a scarce natural resource. The EU depends on imports for more than 90% of its mined phosphorus. Phosphate rock and white phosphorus P4 are both on the EU List of Critical Raw Materials.
The climate related benefits of some of our products are discussed in more detail below.
Applications in animal, fish and pet feed
Traditional vegetable-based feed ingredient production represents the largest share of the carbon footprint of an animal product, particularly for pork, poultry meat, eggs, and farmed fish. Under the EU Green Deal there is a commitment to reduce the EU’s dependency on non-sustainable soya-based feeds.
Extending the utilisation of ABP derived products in animal and fish feed will improve sustainability across the value chain. Using processed animal protein (PAP) and animal fat in farmed animal feed is a low carbon alternative to vegetable-based feeds, with around 10% of the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of soya- based feeds8. In the food waste hierarchy the re-use of ABP derived fats and PAP in animal feed attains the highest value from ABP.
This contributes to reducing the EU’s dependency on non-sustainable imported soybean meal and vegetable oils which are linked to deforestation. Non-sustainable palm and soy cultivation have a relatively high land use change contribution to their climate change impact, which also includes a large share of the agriculture activities associated to their production. This is not the case for our products, with the majority of agriculture and animal farming impact allocated to fresh meat production. The higher digestible protein content of PAP amplifies their benefit per kilogram of protein, an important aspect of feed performance.
EFPRA notes the environmental and sustainability merits of insect meal and its potential to contribute alongside PAPs to reducing the environmental impact of animal feed. We will continue to engage with our animal- based food value chain partners, Government stakeholders and NGOs to promote the use of ABP derived products in feed applications. See EFPRA’s video “Step up Sustainability with Processed Animal Proteins.” which outlines the annual benefits of using PAPs in animal feed, as illustrated in the figure below:

Our products help protect natural resources by replacing fossil carbon, nitrogen, phosphates and non sustainable imported materials such as soya and palm oil, capturing maximum value from natural biological resources.
Pet Food ingredients
Half of all global households now own a cat or dog. There is ever more focus on the welfare of pets and the health and environmental impacts of pet food. Using our products in pet food gives it a lower carbon footprint than using non-sustainable vegetable-based alternatives and makes good use of natural protein, energy and phosphorus content.
Organic fertilisers and soil improvers
Natural, renewable protein fertilisers and soil improvers are recognised for sustainable farming and can replace non-renewable sources. Our fertilisers are particularly valued for phosphorous content helping to close nutrient cycles and reduce mining of rock phosphate.
Biofuel Manufacture
Biofuels made from animal fats can substitute fossil fuels, lowering the environmental impact. Biodiesel manufactured from Category 1 and 2 fats qualifies for RED renewable fuel incentives. Many EFPRA members also generate biogas through anaerobic digestion of various materials.
Biomass Fuels
Category 1 and 2 meat and bone meal (MBM), and tallow can be used as renewable fuels for high energy users such as cement works and power stations. Subject to end of waste regulatory approval, the ash remaining from the combustion of MBM can be used as a fertiliser, a much better option than landfill.
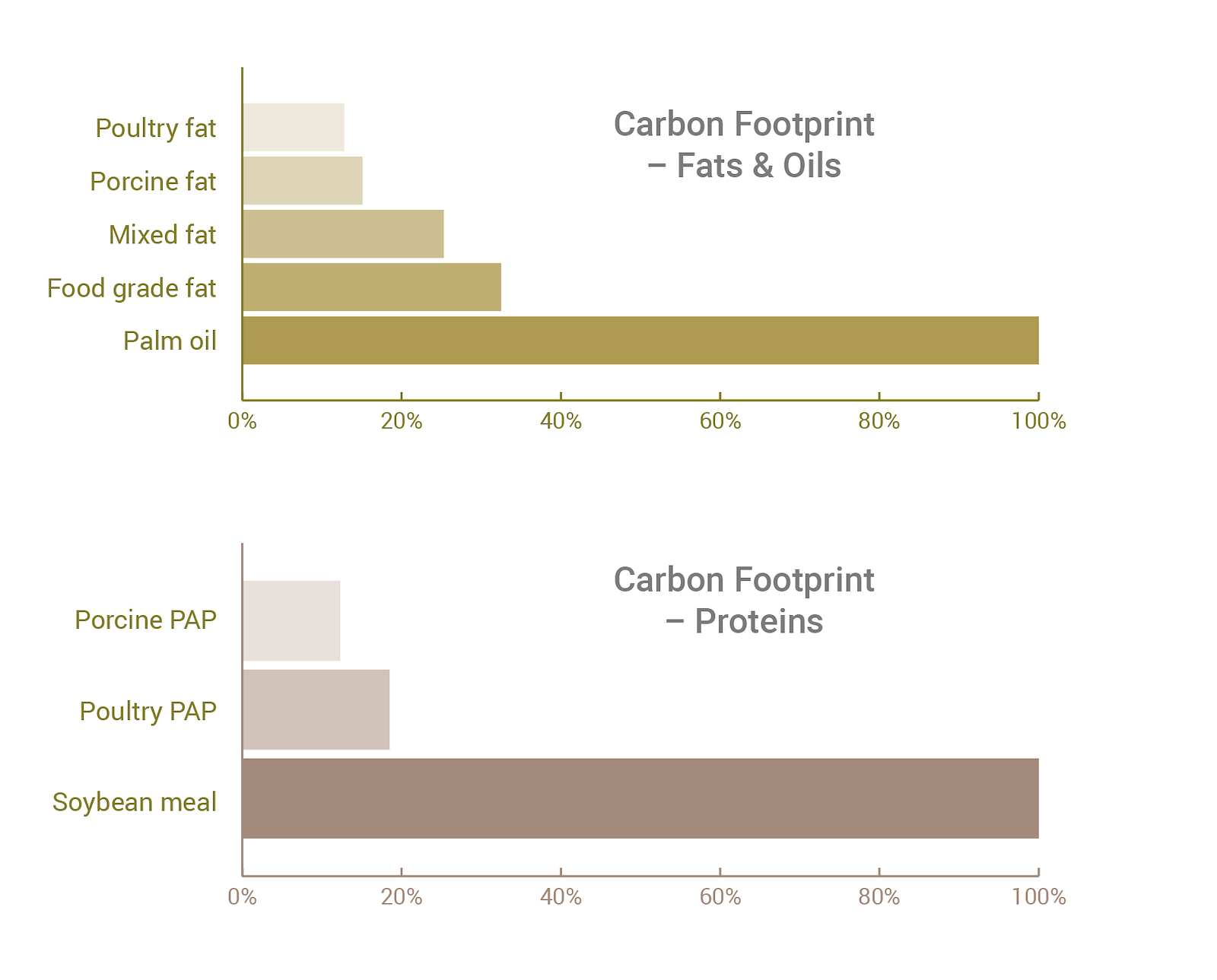
Some of the key climate related sustainability credentials of our ABP derived products are illustrated in the figure below:

Rendering is the only bio-secure option for sanitised collection, transport and treatment of all three categories of ABP which also produces safe, nutritious and valuable low carbon products.